November 24, 2016
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU)
In a unique study, an international team of researchers including members from the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) simulated the violent collisions between supernovae and its surrounding gas— which is ejected before a supernova explosion, thereby giving off an extreme brightness.
Many supernovae have been discovered in the last decade with peak luminosity one-to-two orders of magnitude higher than for normal supernovae of known types. These stellar explosions are called Superluminous Supernovae (SLSNe).
Some of them have hydrogen in their spectra, while some others demonstrate a lack of hydrogen. The latter are called Type I, or hydrogen-poor, SLSNe-I. SLSNe-I challenge the theory of stellar evolution, since even normal supernovae are not yet completely understood from first principles.
Led by Sternberg Astronomical Institute researcher Elena Sorokina, who was a guest investigator at Kavli IPMU, and Kavli IPMU Principal Investigator Ken’ichi Nomoto, Scientific Associate Sergei Blinnikov, as well as Project Researcher Alexey Tolstov, the team developed a model that can explain a wide range of observed light curves of SLSNe-I in a scenario which requires much less energy than other proposed models.
The models demonstrating the events with the minimum energy budget involve multiple ejections of mass in presupernova stars. Mass loss and buildup of envelopes around massive stars are generic features of stellar evolution. Normally, those envelopes are rather diluted, and they do not change significantly the light produced in the majority of supernovae.
In some cases, large amount of mass are expelled just a few years before the final explosion. Then, the “clouds” around supernovae may be quite dense. The shockwaves produced in collisions of supernova ejecta and those dense shells may provide the required power of light to make the supernova much brighter than a “naked” supernova without pre-ejected surrounding material. 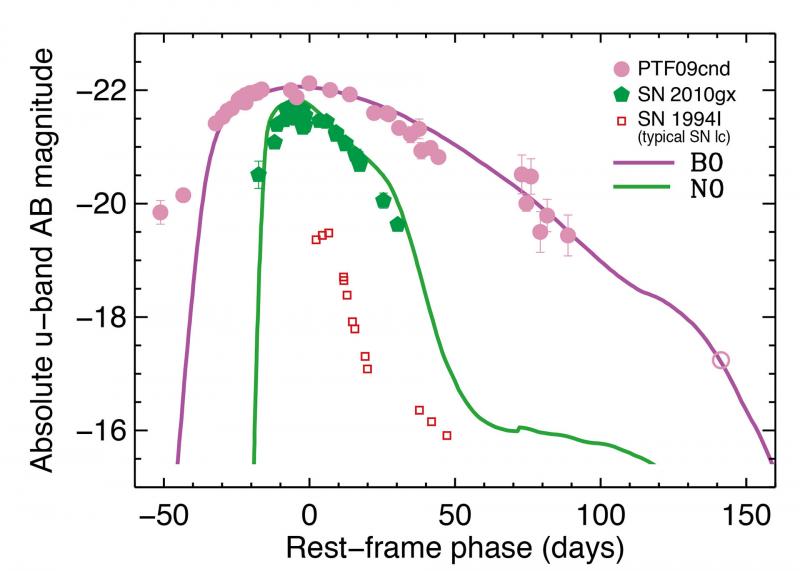
This class of the models is referred to as “interacting” supernovae. The authors show that the interacting scenario is able to explain both fast and slowly fading SLSNe-I, so the large range of these intriguingly bright objects can in reality be almost ordinary supernovae placed into extraordinary surroundings.
Another extraordinarity is the chemical composition expected for the circumstellar “clouds.” Normally, stellar wind consists of mostly hydrogen, because all thermonuclear reactions happen in the center of a star, while outer layers are hydrogenous.
In the case of SLSNe-I, the situation must be different. The progenitor star must lose its hydrogen and a large part of helium well before the explosion, so that a few months to a few years before the explosion, it ejects mostly carbon and oxygen, and then explode inside that dense CO cloud. Only this composition can explain the spectral and photometric features of observed hydrogen-poor SLSNe in the interacting scenario.
It is a challenge for the stellar evolution theory to explain the origin of such hydrogen- and helium-poor progenitors and the very intensive mass loss of CO material just before the final explosion of the star. These results have been published in a paper accepted by The Astrophysical Journal.
Details of the paper were published in September’s The Astrophysical Journal.
Paper Details:
Journal:
The Astrophysical Journal
Title:
Type I Super-luminous Supernovae as Explosions inside Non-Hydrogen Circumstellar Envelopes
Authors:
E.I. Sorokina (1), S.I. Blinnikov (2), K. Nomoto (3), R. Quimby (4), and A. Tolstov (5)
- Elena Sorokina, Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow State University, Universitetsky av. 13, 119234 Moscow, Russia
- S. I. Blinnikov, Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, 117218 Moscow, Russia
- Ken’ichi Nomoto, Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, The University of Tokyo Institutes for Advanced Study, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8583, Japan
- Robert Quimby, Department of Astronomy, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA 92182, USA
- Alexey Tolstov, Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, The University of Tokyo Institutes for Advanced Study, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8583, Japan
DOI: 10.3847/0004-637X/829/1/17 (Published September 15, 2016)
Paper abstract
(The Astrophysical Journal): Link
arXiv.org: 1510.00834, October 2015.
Research contact:
Ken’ichi Nomoto
Principal Investigator and Project Professor
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe
TEL: +81-04-7136-6567
E-mail: nomoto at astron.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
∗change at to @
Alexey Tolstov
Project Researcher
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe
E-mail: alexey.tolstov@ipmu.jp
∗change at to @
Useful links: The Astrophysical Journal
Related links: Kavli IPMU press release: “Magnetar could have boosted explosion of extremely bright supernova”
All images, including those of some of the authors, can be downloaded from here.






